Here is a brief guide to help you distinguish and understand different types of waveplates. If you want more detailed information, please check out our Knowledge Center for a more thorough understanding of waveplates and retarders.
For single wavelength operations, Shalom EO recommends:
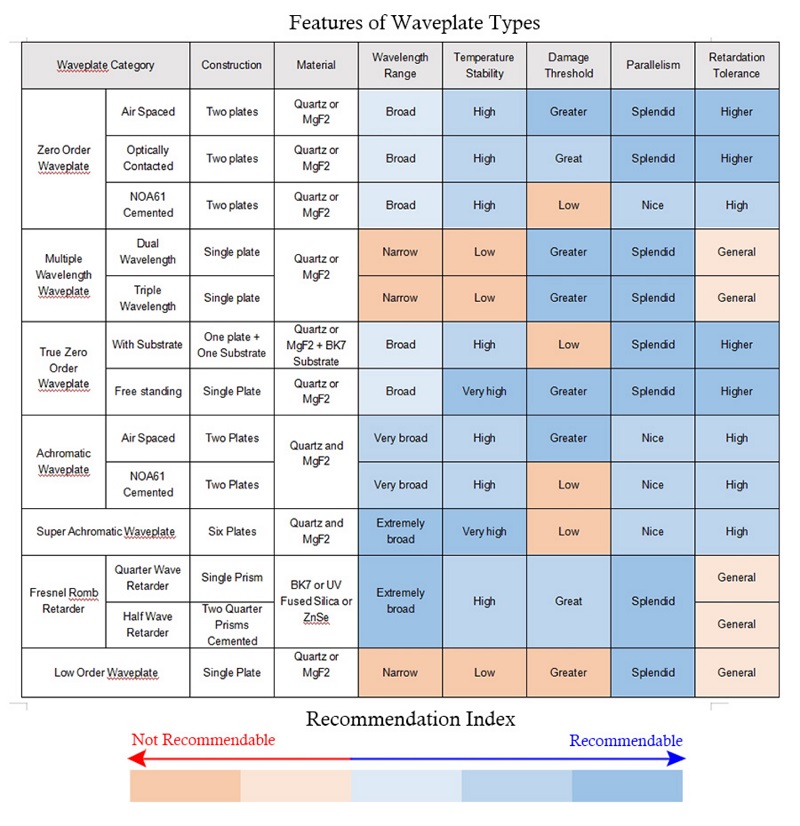
Zero Order Waveplates are comprised of two waveplates with their axes aligned, the resulting retardation have is the difference between two individual retardations. By combining two single waveplates together, Zero Order Waveplates effectively attenuate the impacts of external factor (wavelength change, ambient temperatures) on the desired retardation. However, conventional Zero Order Waveplates will still be influenced by the angle of incidence. Shalom EO offers three types of Zero Order Waveplates: Air spaced Zero Order Waveplates, Optically Contacted Zero Order Waveplates and NOA Cemented Zero Order Waveplates. For high energy operations, consider Air spaced Zero Order Waveplates and Optically Contacted Zero Order Waveplates, since the two types have relatively higher damage threshold than the cemented versions.
True Zero Order Waveplates are ultra-thin waveplates made from quartz or magnesium (MgF2), they provide exactly the required retardation, therefore its thickness is usually only several micrometers. They have more steady retardation performance than conventional Zero Order Waveplates. Shalom EO offers True Zero Order Waveplates made from Quartz (for 532-3000nm) or MgF2 (for long wavelength applications from 3000-7000nm), the single plate versions are fragile but are of high damage threshold, while the versions cemented with BK7 substrates are much easy to handle, but are of lower damage threshold.
Low Order Waveplates are improved versions of multi order waveplates, as the former are much thinner than the latter and possess near zero order performance, but are still more sensitive to dispersion than their zero order counterparts. Low Order Waveplates are cheaper and are an attractive alternative for applications involving large scale producation.
For broadband applications or applications requiring multiple wavelengths, Shalom EO recommends:
Achromatic Waveplates are constructed by one MgF2 Waveplate and one Quartz Waveplates, of which the birefringent properties are complementary and therefore drastically offset the effect of wavelength changes on retardation. They are eminent for various broadband applications including Tunable laser sources, Femto-second laser systems,etc.
Super Achromatic Waveplates consists of six single waveplates (three of Quartz, three of MgF2), they have exceedingly spectrally flat retardation over wide wavelength ranges (standard wavelength ranges 310-1100nm or 600-2700nm)
Fresnel Rhomb Retarders provided by Shalom EO have wide spectral ranges (maximum 2000-15000nm).Fresnel Rhomb Retarders are parallelepiped prisms manufactured from non- birefringent materials. The components of light beam are retarded duing total internal reflections, therefore Fresnel Rhomb Retarder are less susceptible to chromatic dispersion and excellent for broadband applications.
Dual Wavelength Waveplates produces two desired retardation values for two wavelengths through the fitting of the refractive index at different wavelengths. Triple Wavelength Waveplates could also be customized by Shalom EO at your requests.