The manufacturing of Sapphire Windows constitutes a series of complex production stages encompassing drilling, radial-grinding, cutting/slicing, chamfering/beveling, axial-grinding, polishing, and washing/cleaning. These main production stages are summarized below. Some critical production stages including cutting/slicing, tangential grinding, and polishing are explained in more detail.
▶Drilling of Sapphire Windows
Sapphire rods are first gouged out from the bulk single crystals according to the diameters of the sapphire windows. The outlines of the sapphire rods are also different as the window shape varies (e.g. If the final product is a rectangular sapphire, then the sapphire rod should be a cuboid). The gouging tool is often a tube-shaped diamond knife that cuts into the bulk sapphire and sapphire rods are obtained inside the hollow chamber of the diamond knife. On some occasions the bulk sapphire is grown in accordance with the diameters of the window and this step could be skipped.
▶Radial Grinding of Sapphire Windows
It is possible that the side profile of the bulk sapphire or the sapphire rods is not in the ideal precise geometric conditions and the side faces might be too rough and uneven. Grinding wheels with abrasive particles on the grinding front are often hired to grind the trunk of the sapphire rods along the radial direction of the rod.
▶Cutting/Slicing and The Orientations of Sapphire Windows
The orientation of a crystal is a vector describing a random line connecting two nodes on the lattice. Due to the anisotropic nature of crystals, the distribution and the arrangement manner of the atoms change along different directions or upon different lattice planes. The result of this is that the properties and behaviors, even of the same crystals, but with different orientations will differ to a significant extent. This is the reason of choosing the proper orientations and cutting planes of crystals is critical when using crystals to produce various components and elements.
The Sapphire crystals utilized to produce sapphire windows of different functions will be grown and cut/sliced with an engineered orientation, and the orientation is often determined because it will optimize the crystal’s performance to achieve the intentions of interest.
The lattices within the sapphire are arranged in a hexagonal structure. When a sapphire element is produced, the direction of its inner architecture affects the functionalities of the element.
The common orientation of sapphire windows is “a”, “c”, “n”, and “m”, as shown in the figure below.
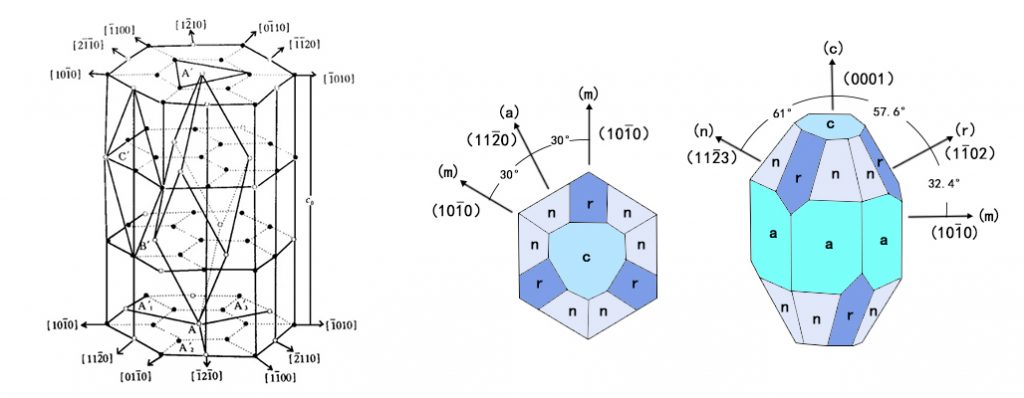
Figure 1.The Lattice Structure of Sapphire and Common Sapphire Crystal Orientations

